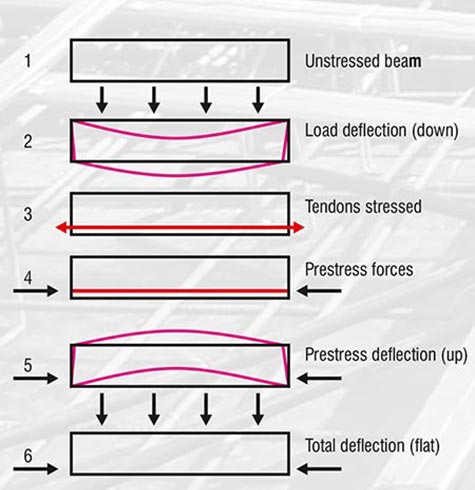
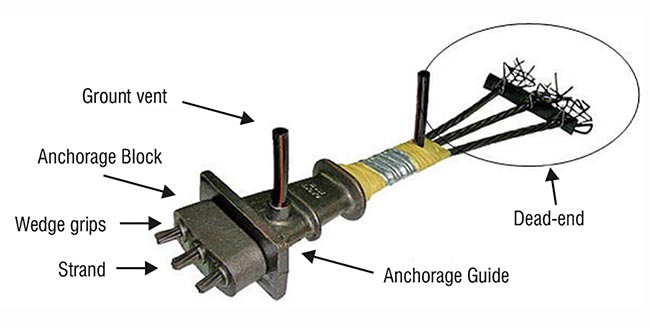
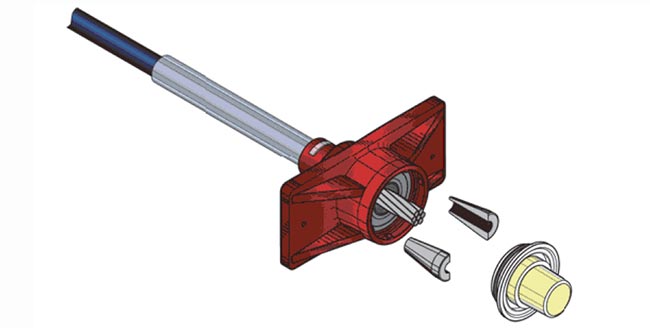
Post Tensioning Concept
PT – Post tensioning is a method of reinforcing (strengthening) concrete with high-strength steel strands or cables, typically referred to as tendons. Post-tensioned concrete is a variant of prestressed concrete where the tendons are tensioned after the surrounding concrete structure has been cast. The essence of prestressed concrete is that once the initial compression has been applied, the resulting material has the characteristics of high-strength concrete when subject to any subsequent compression forces, and of ductile high-strength steel when subject to tension forces. This can result in improved structural capacity and/or serviceability compared to conventionally reinforced concrete in many situations.